Industrial drying is one of the most essential processes across manufacturing, agriculture, mining, chemicals, and many other sectors. Whether it’s removing moisture from minerals, drying fertilizers, processing biomass, or ensuring food ingredients reach the desired moisture level—drying plays a crucial role in improving product quality and shelf life.
Among all drying technologies available today, the rotary dryer stands out as one of the most efficient, versatile, and widely used industrial drying machines.
In this blog, you will learn what a rotary dryer is, how it works, its types, uses, advantages, applications, and why industries prefer it over other drying systems.
This complete guide is written in simple language, making it easy even for beginners to understand.
What Is a Rotary Dryer?
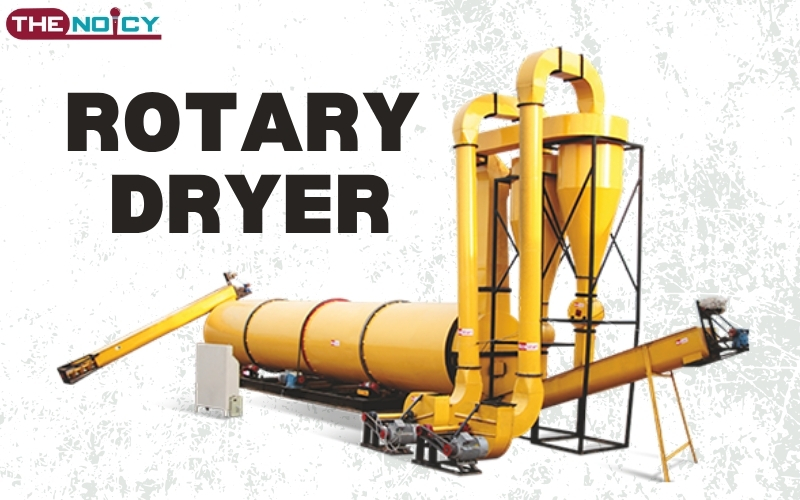
A rotary dryer is a cylindrical drying machine that rotates slowly to dry bulk solids. It uses hot gas or air to remove moisture from the material. The drum is slightly inclined, which allows the material to move from the feed end to the discharge end.
Here’s a simple explanation:
-
Material enters the rotating drum.
-
Hot air flows inside the drum.
-
The drum rotates and lifts the material using internal lifters.
-
As the material falls through the hot air, moisture evaporates.
-
The dried material exits from the other end.
Rotary dryers can handle a wide variety of materials—wet, sticky, hard, abrasive, or heat-sensitive—making them extremely versatile.
How Does a Rotary Dryer Work? (Step-by-Step Working Explained)
The working of a rotary dryer is very simple but extremely efficient. Here’s how it functions step by step:
1. Feeding the Material
The wet material is fed into the rotary dryer using a conveyor, feeder, or screw mechanism.
It enters through the feed inlet located at the higher end of the inclined drum.
Materials commonly fed into a rotary dryer:
-
Sand
-
Minerals
-
Coal
-
Fertilizers
-
Biomass
-
Limestone
-
Food ingredients
-
Chemicals
2. Rotation of the Drum
Once the material enters, the drum rotates at a slow speed.
Rotation is important because it:
-
Keeps the material in motion
-
Prevents sticking or clumping
-
Ensures uniform exposure to heat
Inside the drum, special plates known as lifting flights pick up and drop the material continuously.
This creates a “shower” of material, increasing the surface area for drying.
3. Hot Airflow or Heat Source
The rotary dryer uses one of the following to generate heat:
-
Hot air
-
Steam
-
Gas burners
-
Biomass burners
-
Waste heat from industrial processes
The air can flow in two ways:
Co-current Flow
Hot air and materials move in the same direction.
Best for heat-sensitive materials.
Counter-current Flow
Hot air and materials move in opposite directions.
Best for materials requiring high heat.
4. Evaporation of Moisture
As hot air passes through the tumbling material, moisture begins to evaporate.
This process depends on:
-
Temperature
-
Humidity
-
Drum speed
-
Material type
-
Residence time
The rotary dryer ensures maximum contact between air and material, making drying faster and more efficient.
5. Movement of Material Toward the Outlet
Because the drum is set at a slight angle, gravity helps the material move towards the discharge end.
The material becomes gradually drier as it moves along the drum.
6. Discharge of Dried Material
At the end of the drum, dried material exits through the discharge outlet.
It may go to:
-
Storage silos
-
Conveyors
-
Screening units
-
Cooling machines
7. Exhaust System
A fan removes moisture-laden air from the dryer.
Dust collectors or cyclones ensure that fine particles don’t escape into the environment.
Types of Rotary Dryers
Rotary dryers come in multiple designs depending on material type and drying needs.
1. Direct Rotary Dryer
Hot air directly contacts the material.
Used for:
-
Minerals
-
Sand
-
Coal
-
Fertilizers
2. Indirect Rotary Dryer
Heat is transferred through the drum wall (no direct air contact).
Used for:
-
Fine powders
-
Toxic materials
-
Heat-sensitive materials
3. Rotary Drum Dryer
A general-purpose dryer with lifting flights inside.
Used across most industries.
4. Steam Tube Rotary Dryer
Uses steam inside tubes for gentle drying.
Ideal for:
-
Food materials
-
Chemicals
-
Organic substances
5. Triple-Pass Rotary Dryer
Three concentric drums improve drying efficiency and save fuel.
Uses and Applications of Rotary Dryers
Rotary dryers are used in almost every industrial sector.
Here are the major applications:
1. Agriculture
Rotary dryers help dry:
-
Crop residues
-
Seeds
-
Grains
-
Organic fertilizers
This prevents spoilage and improves storage.
2. Mining and Minerals
Industries use rotary dryers to remove moisture from:
-
Limestone
-
Sand
-
Clay
-
Coal
-
Iron ore
-
Bauxite
Drying enhances product quality and efficiency during processing.
3. Chemical Industry
Used for powders, granules, and chemical compounds.
Rotary dryers ensure controlled moisture levels for accurate chemical reactions.
4. Fertilizer Industry
Rotary drum dryers dry:
-
NPK fertilizers
-
Organic fertilizers
-
Ammonium compounds
They help maintain uniform granule size and prevent caking.
5. Biomass and Energy Industry
Rotary dryers process:
-
Sawdust
-
Wood chips
-
Bagasse
-
Crop waste
This is crucial for producing briquettes, pellets, and biofuels.
6. Food Processing
Used for drying:
-
Grains
-
Spices
-
Fibers
-
Starch products
Ensures longer shelf life and safety.
7. Construction Materials
Helps dry:
-
Cement mixtures
-
Fly ash
-
Slag
-
Gypsum
Key Benefits of a Rotary Dryer
1. Handles a Wide Range of Materials
Rotary dryers can dry fine powders, granules, large solids, sticky materials, and abrasive particles with ease. Their ability to process different material types makes them ideal for industries such as minerals, chemicals, agriculture, and biomass, ensuring stable performance under varying conditions.
2. High Drying Capacity
Designed for continuous operation, rotary dryers can handle large volumes of material effortlessly. Their rotating drum ensures fast moisture removal, making them perfect for industrial settings that require uninterrupted drying and high production output around the clock.
3. Uniform and Consistent Drying
The internal lifting flights lift and drop the material inside the drum, allowing even exposure to hot air. This constant movement prevents clumping, ensures every particle dries uniformly, and achieves consistent moisture levels, improving the final product quality significantly.
4. Energy-Efficient Performance
Rotary dryers use optimized heat transfer, controlled airflow, and optional triple-pass systems to reduce fuel consumption. Their design helps industries lower energy costs while still maintaining quick and effective drying results, making them one of the most economical drying solutions.
5. Low Maintenance Requirements
With a strong structure and fewer complex components, rotary dryers are easy to maintain. Routine lubrication and inspections are enough to keep them running efficiently. Their durability reduces maintenance downtime, repair expenses, and overall operational interruptions.
6. Continuous 24/7 Operation
Rotary dryers are built for continuous use, making them ideal for industries with high production demands. They run smoothly without frequent stopping or cleaning, maintaining steady output and ensuring reliable performance throughout long operational cycles.
7. Suitable for High-Moisture Materials
Rotary dryers can efficiently dry materials with extremely high moisture content, even up to 70%. Their design allows moisture to evaporate quickly, making them perfect for drying biomass, minerals, fertilizers, and agricultural products that start with heavy wetness.
8. Customizable to Industry Needs
Rotary dryers can be customized in drum size, airflow type, heat source, residence time, and internal flight design. This flexibility ensures that each dryer is optimized for specific materials and drying goals, delivering maximum efficiency for every industry application.
Why Rotary Dryers Are Better Than Other Dryers?
Rotary dryers are often compared with fluid bed dryers, spray dryers, and flash dryers.
Here’s why industries prefer rotary dryers:
-
Lower maintenance
-
Higher durability
-
Can handle larger particle sizes
-
Better for abrasive materials
-
More cost-effective over long term
-
Can operate in harsh environments
Rotary dryers outperform other dryers in terms of versatility, lifespan, and drying capacity.
Challenges in Rotary Dryers (and Their Solutions)
Even though rotary dryers are efficient, some issues may occur:
1. Material sticking inside the drum
Solution: Install proper lifting flights and adjust drum speed.
2. Over-drying or under-drying
Solution: Monitor temperature, feed rate, and residence time.
3. Dust generation
Solution: Use cyclones, bag filters, or dust collectors.
4. Heat loss
Solution: Insulate the drum and use triple-pass designs.
Maintenance Tips for Long Life
To ensure the rotary dryer runs smoothly for years, follow these maintenance practices:
-
Check drum alignment regularly
-
Lubricate bearings and gears
-
Inspect lifting flights for wear
-
Monitor temperature and airflow
-
Clean dust collectors frequently
-
Check seals and replace damaged ones
Proper maintenance increases efficiency and avoids costly breakdowns.
Future Scope of Rotary Dryers
With the rise of renewable energy and sustainable manufacturing, rotary dryers will remain crucial.
Trends for the future include:
-
More energy-efficient designs
-
Use of alternative fuels
-
Smart monitoring systems
-
Eco-friendly heat recovery technologies
Industries are adopting rotary dryers because they offer consistent output with lower operational costs.
You Can Also Read: What Is a Mock Drill and Why It’s Important
Conclusion
A rotary dryer is one of the most reliable and versatile industrial drying machines used today. Its simple design, high capacity, and ability to dry various materials make it an essential equipment across industries like agriculture, mining, chemicals, fertilizers, food processing, and biomass.
Whether you want to reduce moisture, improve product quality, or increase production efficiency, a rotary dryer delivers excellent results.
With proper maintenance and customization, it can serve industries for decades.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. How does a rotary dryer work?
Ans: A rotary dryer works by rotating a drum while hot air flows through it. As the drum turns, lifting flights raise and drop the material, allowing heat to evaporate moisture evenly and efficiently.
2. What is a rotary dryer?
Ans: A rotary dryer is an industrial drying machine that reduces moisture in bulk materials such as minerals, fertilizers, biomass, and chemicals using a rotating drum and hot air.
3. What is a steam tube rotary dryer?
Ans: A steam tube rotary dryer uses steam inside tubes running through the drum to heat and dry materials indirectly. It is ideal for heat-sensitive materials, chemicals, and organic products.
4. What is NTU in rotary drum dryers?
Ans: NTU (Number of Transfer Units) measures the effectiveness of heat transfer inside a rotary dryer. A higher NTU means better efficiency and faster drying performance.
5. How to set up a rotary dryer?
Ans: To set up a rotary dryer, position the drum structure, connect the heat source, attach airflow systems, align the drum correctly, install the feeder and discharge units, and run test cycles to ensure proper rotation and drying.
6. How do rotary dryers work in industrial applications?
Ans: In industrial use, rotary dryers continuously feed wet material into the rotating drum where hot air removes moisture. This system handles large volumes and provides uniform, controlled drying.
7. What is a rotary vacuum dryer?
Ans: A rotary vacuum dryer dries materials under low pressure, allowing moisture to evaporate at lower temperatures. It is used for sensitive chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and materials that cannot be exposed to high heat.
8. What are the benefits of using a rotary dryer?
Ans: Rotary dryers offer high capacity, uniform drying, energy efficiency, low maintenance, continuous operation, and the ability to handle diverse materials, making them ideal for many industrial processes.
9. What size rotary dryer do I need for industrial use?
Ans: The required size depends on material moisture, feed rate, density, and desired drying capacity. Large drums are used for high-volume applications, while smaller drums suit moderate production needs.
10. What is the best type of rotary dryer for industrial materials?
Ans: For minerals and bulk solids, direct rotary dryers are best. For heat-sensitive materials, indirect or steam tube dryers are preferred. The best type depends on material properties and drying goals.